03/07/2016
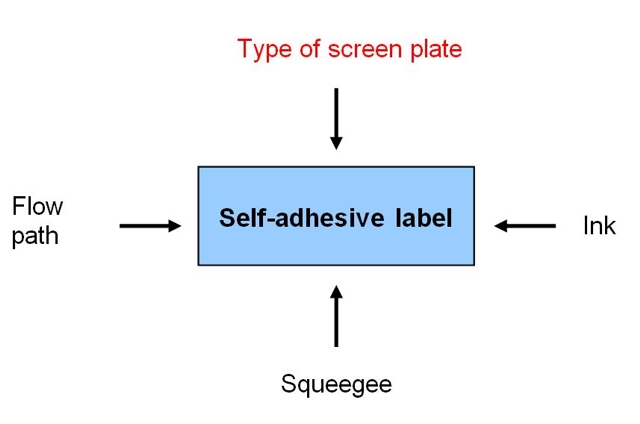
To achieve a good printing result, it is important to pay particular attention to the most important factors influencing rotary screen printing. The decisive factors are the type of screen plate, the ink, the squeegee, and the travel distance. Today's article will focus on the type of screen plate, which is the variable that has the greatest influence on the print image. By selecting the right screen, the printer can control this variable accordingly.

-2.jpg)
-2.jpg)
The screen printing plate regulates the volume of the ink layer that is transferred to the substrate. Gallus Screeny screen printing mesh is made of steel and is manufactured in special weaving mills. The same terminology is used for woven stainless steel mesh as for woven textiles. It therefore consists of weft and warp threads (see sketch).
.jpg)
.jpg)
The more evenly the fabric is woven, the more accurately the desired color volume is transferred to the substrate. It is therefore important that the warp and weft threads are woven in such a way that they always form a square mesh. If, for example, large color pigments are to be pressed through the screen fabric, this homogeneous structure is of crucial importance.
"A" has the same length as "B."
.jpg)
The steel mesh itself is a very fragile structure. In order to be used for rotary screen printing, it must be reinforced using a galvanization process, whereby it is coated with a complete and homogeneous layer of nickel. Experience has shown that the galvanized mesh only has a high degree of stability and optimal ink flow if the steel mesh is evenly and smoothly coated with this nickel layer.
The close-up shows a homogeneous, smooth nickel surface of the fabric.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
After the steel mesh has been nickel-plated, it is coated over its entire surface with a photopolymer layer in a clean room. It is important that the photopolymer coating has no gaps and is of a consistent thickness across the entire screen mesh (EOM = emulsion over mesh). If these basic requirements are not met, it will not be possible to achieve a defined and precisely controlled ink transfer.
The uniformly applied and closed photopolymer layer is a necessary quality factor for a rotary screen printing plate.
.jpg)
The combination of perfectly woven and galvanized stainless steel mesh and a closed, homogeneous photopolymer layer provides the necessary basis for achieving precise color control in screen printing. After the photopolymer layer has been exposed and washed out, the required ink volume is pressed through the openings of the galvanized stainless steel mesh.
The green polymer layer controls the targeted flow of the yellow ink droplets.
.jpg)
But what criteria does the label printer use to select the right screen printing plate for the application in question? Three factors play a decisive role in this selection: the ink layer thickness, the resolution, and the size of the ink pigment. In terms of ink layer thickness, Gallus offers a range of Gallus Screeny screen printing plates with ink build-up from 5 to 280 microns. The resolution of the ink pigment, which is very important because rotary screen printing is still mainly used for solid and line motifs, can be varied from 100 to 400 microns with Gallus Screeny screen printing plates. Finally, for the size of the ink pigment to be pressed through the screen mesh, the Gallus Screeny screen printing plates offer a range from 24 to 265 microns.
.jpg)
An uneven photopolymer layer causes holes in the print image. During exposure and subsequent washing out of the screen, parts of the photopolymer layer are washed out, so that the screen printing plate must be manually reworked with a photopolymer filler before it can be mounted on the printing machine. An industrially manufactured screen printing plate should always have a smooth, homogeneous, and closed photopolymer layer.
.jpg)
Thanks to its pioneering role in rotary screen printing and its many years of experience in this field, Gallus is the right partner to contact if you have any questions about your rotary screen printing plate. Gallus Screeny offers the most comprehensive range of screen printing plates for rotary screen printing on narrow web label printing presses. The Gallus Screeny team will be happy to advise you on the selection of the most suitable screen printing plate type for your application.
03/07/2016
To achieve a good printing result, it is important to pay particular attention to the most important factors influencing rotary screen printing. The decisive factors are the type of screen plate, the ink, the squeegee, and the travel distance. Today's article will focus on the type of screen plate, which is the variable that has the greatest influence on the print image. By selecting the right screen, the printer can control this variable accordingly.
The screen printing plate regulates the volume of the ink layer that is transferred to the substrate. Gallus Screeny screen printing mesh is made of steel and is manufactured in special weaving mills. The same terminology is used for woven stainless steel mesh as for woven textiles. It therefore consists of weft and warp threads (see sketch).
The more evenly the fabric is woven, the more accurately the desired color volume is transferred to the substrate. It is therefore important that the warp and weft threads are woven in such a way that they always form a square mesh. If, for example, large color pigments are to be pressed through the screen fabric, this homogeneous structure is of crucial importance.
"A" has the same length as "B."
The steel mesh itself is a very fragile structure. In order to be used for rotary screen printing, it must be reinforced using a galvanization process, whereby it is coated with a complete and homogeneous layer of nickel. Experience has shown that the galvanized mesh only has a high degree of stability and optimal ink flow if the steel mesh is evenly and smoothly coated with this nickel layer.
The close-up shows a homogeneous, smooth nickel surface of the fabric.
After the steel mesh has been nickel-plated, it is coated over its entire surface with a photopolymer layer in a clean room. It is important that the photopolymer coating has no gaps and is of a consistent thickness across the entire screen mesh (EOM = emulsion over mesh). If these basic requirements are not met, it will not be possible to achieve a defined and precisely controlled ink transfer.
The uniformly applied and closed photopolymer layer is a necessary quality factor for a rotary screen printing plate.
The combination of perfectly woven and galvanized stainless steel mesh and a closed, homogeneous photopolymer layer provides the necessary basis for achieving precise color control in screen printing. After the photopolymer layer has been exposed and washed out, the required ink volume is pressed through the openings of the galvanized stainless steel mesh.
The green polymer layer controls the targeted flow of the yellow ink droplets.
But what criteria does the label printer use to select the right screen printing plate for the application in question? Three factors play a decisive role in this selection: the ink layer thickness, the resolution, and the size of the ink pigment. In terms of ink layer thickness, Gallus offers a range of Gallus Screeny screen printing plates with ink build-up from 5 to 280 microns. The resolution of the ink pigment, which is very important because rotary screen printing is still mainly used for solid and line motifs, can be varied from 100 to 400 microns with Gallus Screeny screen printing plates. Finally, for the size of the ink pigment to be pressed through the screen mesh, the Gallus Screeny screen printing plates offer a range from 24 to 265 microns.
An uneven photopolymer layer causes holes in the print image. During exposure and subsequent washing out of the screen, parts of the photopolymer layer are washed out, so that the screen printing plate must be manually reworked with a photopolymer filler before it can be mounted on the printing machine. An industrially manufactured screen printing plate should always have a smooth, homogeneous, and closed photopolymer layer.
Thanks to its pioneering role in rotary screen printing and its many years of experience in this field, Gallus is the right partner to contact if you have any questions about your rotary screen printing plate. Gallus Screeny offers the most comprehensive range of screen printing plates for rotary screen printing on narrow web label printing presses. The Gallus Screeny team will be happy to advise you on the selection of the most suitable screen printing plate type for your application.